Introduction
If you are finding Why do we fall ill Notes and extra questions for class 9 with ncert solutions then you are at the right place.
Here we will provide you best and selected
Notes of why do we fall ill class 9 and why do we fall ill class 9 extra questions with ncert solutions.
Topics we are going to cover
- Health
- Personal and community Health disease
- Disease
- Infectious Diseases
- Immunisation
- Pulse Polio Programme
Join our telegram channel for daily updates and lots of study material in free of cost.
Notes of Why Do We Fall ill Class 9
■ Health
- Health is a state of physical, mental and social well-being.
► Basic conditions for good health
(i) Proper balanced and nutritious diet
(ii) Personal hygiene
(iii) Clean environment and sorroundings
(iv) Healthy air, no pollution in the sorroundings
(v) Regular exercise
(vi) Proper rest
(vii) Good standard of living and economic status
■ Difference between Being "Healthy and "Disease-free"
Being Healthy
- It is a state of being well enough to function well physically, mentally and socially.
- It refers to the individual, physical and social environment.
Being Disease free
- It is a state of absence from disease.
- It refers only to the individual.
Let's practice (questions from the topic)
- How does balanced diet played a important role in protecting us from disease and keeping us healthy?
- Why does we say that good economic condition and social harmony are needed for a person to achieve individual health?
- It has been said that personal and community health go hand in hand. Do you agree? If yes, how?
- Can you suggest various measures for maintaining community healthy?
- Explain, how does better public cleanliness lead to better community health.
- How is health education helpful in maintaining better community health?
- Using a point of difference, state how being healthy is different from being disease-free?
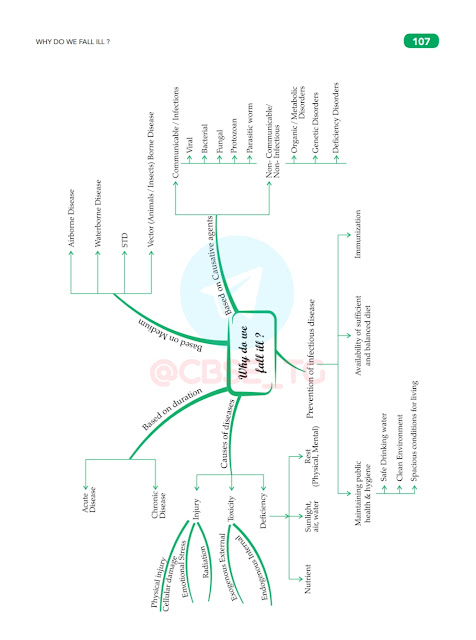
■ Disease
- It is a lack of ease i.e person is uncomfortable. If our body organs are not functioning Properly, we are suffering from disease.
► Types of disease
On The Basis Of Time Period
(i) Acute disease
- They last for short period
- They don't cause long term bad effect on human health
- Example: Common cold, cough etc.
(ii) Chronic disease
- They last for short period
- They cause long term bad effect on human health
- Example: Diabetes, Tuberculosis etc.
On The Basis Of Causative Factor
(i) Infectious disease
- They are caused by microorganisms
- Transmission through air, water, physical contact
- Infection may spread to a healthy person
- Example: AIDS, Tetanus etc.
(ii) Non - Infectious disease
- These are caused by environmental changes
- Transmission is not possible
- Infection do not spread
- Example: Cancer, Heart disease etc.
Let's practice (questions from the topic)
- On what basis you can analyse that one or more body organs of a person are not functioning properly?
- What helps a physician to confirm a disease?
- When compared to an acute disease patient, a chronic disease patient recover after a longtime. Is it true? Explain.
- State the relation between inadequate diet and health, with an example.
- How does lack of public services and poor economic conditions responsible for causing a disease? Support with an example.
- Do all disease spread to people coming in contact with a sick person?
- What are the various type of disease that has the property of remaining restricted only to a particular person.
■ Paptic Ulcer
- Caused due to Helicobacter pylori which is a bacteria
- Discovered by Barry Marshall and Robin Warren.
Due to their discovery peptic ulcer is no longer a chronic disease
 |
| helicobacter pylori |
(iii) Congenital disease
- These are passed on from parents to their offspring genetically
- Example: Haemophilia
(iv) Acquired disease
- These are not passed on from parents to their offspring genetically
- Example: Diabetes
► Causes of Diseases
- Pathogens like virus, bacteria, fungi, protozoans or worms
- Poor health and under nourishment
- Hereditary and genetic disorder
- Lack of proper treatment of immunization
- Environmental pollution
► Disease causing organism
(i) Virus: It can cause common cold, chicken pox, AIDS etc.
(ii) Protozoa: Protozoans like Trypanosoma causes sleeping sickness and Leishmania causes Kala-azar. Protozoa also causes malaria(Plasmodium), amoebic etc.
 |
| Trypanosoma |
 |
| Leishmania |
(iii) Vectors: Some organism like female Anopheles mosquito act as a carrier of disease like malaria, and aedes mosquito act as a carrier of dengue, yellow fever etc.
(iv) Sexual contact: Syphilis, AIDS spread by sexual contact with infected person. AIDS can also spread through blood transfusion and from the infected mother to her child during pregnancy.
(v) Rabid animals: Rabies is spread through the bite of animal(dog).
Very Important Tables
- The drugs which are obtained from microorganisms and are used to kill or suppress the multiplication of microorganisms are called Antibiotics.
- Organisms such as Protozoa and fungi can be used to prepare antibiotics
■ How antibiotics works?
- Many bacteria, make a cell - well to protect themselves. The antibiotic penicillin blocks the bacterial processes that build the cell wall. As a result, the growing bacteria becomes unable to make cell - walls and die easily. Human cells don't make a cell - well anyway, So penicillin will have this effect on any bacteria that use such processes for making cell - walls. Similarly, many antibiotics work against many species of bacteria rather than simply working against one.
- Viruses do not use these pathways and therefore antibiotics do not work against viral infections.
- Example: Tetracycline, Penicillin, Streptomycin etc.
■ AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency System)
AIDS is caused by a retro - viruses called HIV (Human Immuno Deficiency Virus).
- Method of transmission of AIDS
(i) Through Unsafe Sexual contact
(ii) Through Blood transfusion
(iii) By The Use of infected syringe or blade
(iv) This may also get transmitted from infected mother to her child during pregnancy through her placenta or through breastfeeding .
(i) Avoid sexual contact to unknown person
(ii) Avoid transfusion of infected blood. This can be done by testing whether the blood is HIV negative or not.
(iii) Always use disposable needle and syringe
■ Organ - specific and tissue specific manifestations
- Disease causing microbes enter the body by different means and goes to different organs and tissues.
Microbes which enter the body by different means and goes to different organs and tissues.
Soe of them are :-
(i) Microbes which enter through the nose are likely to go to the lungs. (Bacteria which cause tuberculosis of lungs).
(ii) Virus which causes AIDS enter the body through sexual organs during sexual contact and spread through the lymph to all parts of the body and damages the immune system.
(iii) The virus causing Japanese encephalitis (brain fever) enters the body through mosquito bite and goes to infects the brain.
■ Immune system
It is a defence mechanism of the body to fight against the infection by creating antibodies.
■ Immunisation
If you had smallpox once, there was no chance of suffering from it again .So, having the disease once was a means of preventing subsequent attacks of the same disease. This happens because when the immune system first sees an infectious microbe, it responds against it and then remembers it specifically. So the next time that particular microbe, or its close relatives enter the body, the immune system responds with even greater vigour. This eliminates the infection even more quickly than the first time around. This is also known as immunisation.
Let's practice (questions from the topic)
- State the purpose behind dividing the infectious diseases into different categories.
- One antibiotic can work against many species of bacteria rather than simply working against one Justify.
- Discuss ways in which microorganisms can find entry into human body.
- Why female Anopheles mosquito feed on blood of warm - blooded animals like human beings?
- Keeping in mind about the property of organ - specific diseases. Mention the location of the microbes when they enter through nose, mouth and sexual contact respectively.
- A person complaints of frequently headache vomiting and becomes unconscious frequently. Which organ is most likely to be affected?
- Do you agree that the severity of disease manifestations indirectly depends on the number of microbes in the body? If yes, explain how?
- Immune system is a major factor determining the number of microbes in body.
■ Principles of treatment
There are two ways of treatment:-
(i) To reduce the effect of the disease: This can be done by taking medicines to bring own the effect of the disease like fever, pain etc. and by taking bed rest to conserve our energy.
(ii) To kill the microbes: This can be done by taking suitable antibiotics and drugs which can kill the microbes.
■ Principle of prevention
- Proper balanced and nutritious diet
- Public hygiene
- Clean environment and surroundings
- Healthy air, no pollution in the surrounding
- Proper sanitation
- Safe drinking water
- Pest control
It is done by Immunization. This is the process of introducing a weakened pathogen inside the body of the host to fool his/her immune system to produce antibodies against that Particular disease.
Symptoms
Symptoms of disease are the things we feel as being 'wrong' like headache, cough etc. These indicate that there may be a disease but they do not exactly indicate what the disease is but they narrow the possibilities of certain diseases . symptoms are felt by the host body and can't be seen by anyone else.
Signs
Signs give more definite indications of the presence of a particular disease ,which help the doctors (physicians) to diagnose the diseases. Signs can be seen by others such as inflammation heating body.
Let's practice (questions from the topic)
- Giving treatment to reduce the symptoms of a disease is not enough in order to cure a person, killing of microbe is also essential. Explain.
- Do you agree with the fact that anti-viral bacterial medicines? If yes, why?
- Write the limitation to be kept in mind, while treating an infectious disease.
- What are the practices to prevent airborne microbes?
- State the major practice one should adopt in order to reduce vectorborne microbes.
- Severe infectious disease represents the failure of the immune system. Comment.
- Give the logical explanation behind eliminating the infection more quickly when it enters the second time into the body.
- State the phenomenon of working of vaccine in human beings.
- Is there any difference between immunisation and vaccination? If yes, explain.
- Hepatitis - A vaccine was given to a child of 8 years. Will it be helpful? Give reason.
Pulse Polio Programme
- India launched the Pulse Polio Immunisation (PPI) programme in 1995 as a result of World Health Organisation (WHO) Global Polio Eradication Initiative.
- In this programme, all the childerns who are under 5 years are given two drops of Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) in December and January every year until polio is eradicated.
- PPI was initiated with the objective of achieving hundred percent coverage.
- India has been declared polio-free by WHO.
- Pulse Polio Programme is continuing to eliminate any chance of its comeback.
I hope you like the Notes of why do we fall ill class 9 term 2. Let us know in comment section.
Why do we fall ill class 9 extra questions with ncert solutions
Why do we fall ill Class 9 Ncert solutions
Question 1. State any two conditions essential for good health.
Answer: (i) Health is a condition of human being in which he is free from any illness and is felling well.
(ii) Conditions essential for good health are:
(a) Balanced and nutritious diet
(b) Social and healthy environment
Question 2. State any two conditions essential for being free of disease.
Answer: Conditions essential for being free of disease are:
(i) Taking balanced and nutritious diet.
(ii) Living in a good, social, clean and healthy environment.
Question 3. Are the answers to the above questions (Q. 1 and Q. 2) necessarily the same or different? Why?
Answer: (i) The answer to the above questions (Q. 1 and Q. 2) is same to some extent. Because if the conditions that are essential for good health are maintained then automatically the chances of getting disease will be minimised.
(ii) But at the same time, the answers are different because good health means the state of good physical, mental and emotional well-being whereas disease fee means not suffering from any disease
Question 4. List any three reasons why you would think that you are sick and ought to see a doctor. If only one of these symptoms were present, would you still go to the doctor? Why or why not?
Answer: (i) Common symptoms will make us to feel sick and make us think to see a doctor are :
(a) Cold and cough
(b) Loose motion
(c) Fever
(d) Headache
(ii) Moreover, it depends on the type of symptoms also. Because few symptoms, like headache or cold, do not have much effect on our daily life routine or our general health.
(iii) However, if anyone symptoms persist for more than 2–3 days then definitely we should visit to doctor for its further investigation and proper treatment.
Question 5. In which of the following case do you think the long-term effects on your health are likely to be most unpleasant?
(i) if you get jaundice.
(ii) if you get lice.
(iii) if you get acne.
Why?
Answer: (i) In case of jaundice, the long-term effects on health are likely to be the most unpleasant.
(ii) Because,
(a) Jaundice is a chronic disease and takes long time to be completely cured.
(b) Moreover, it affects the whole body,
especially liver, the most important part of
our body.
(iii) Whereas lice and acne are acute problems of health which can be cured in a short period of time.
Question 6. Why are we normally advised to take bland and nourishing food when we are sick?
Answer: We are advised to take bland and nourishing food when we are sick because our body needs energy to overcome the infection and the wear and tear of body organ. A nourishing food is easily digestible and contains all the nutrients. So, it provides nutrients to our body that will further provide energy and make new cells.
Question 7. What are the different means by which infectious diseases are spread?
Answer: (i) Infectious disease may occur due to the presence and activity of a pathogenic microbial agent like
bacteria, virus and protozoa.
(ii)It can be spread from one person to another, through the following means :
(a) Air : Disease transferred from air (through sneezing and coughing) is
generally called air-borne disease. For example, common cold and pneumonia.
(b) Water and food : Disease caused due to
contaminated food and water is called
water-borne disease. It can cause disease
like cholera and typhoid.
(c) Contact : Many diseases spread by contact of infected person with the healthy person. For example, fungal infections, scabies and skin disorder.
(d) Sexual contact : These are called sexually transmitted diseases, for example, AIDS and syphilis.
(e) Animals : These are referred to as vectors that spread disease by carrying pathogen from one place to another, for example, mosquitoes are vectors which carry pathogen-like protozoa (e.g., Plasmodium sp.) and causes malaria.
Question 8. What precautions can you take in your school to reduce the incidence of infectious diseases?
Answer: The precautions you can take in your school to reduce the incidence of infectious diseases are:
Preventing over-crowding classes.
(ii) Getting vaccinating before the infection affects.
(iii) Using clean toilets to prevent getting infection from there.
(iv) Staying at home if anyone suffers from
infectious disease.
(v) Avoiding food which are exposed to flies or mosquitoes.
(vi) Drinking safe and clean water and washing hands before eating tiffin.
(vii) Avoid mosquito breeding by preventing water to stagnate in school premises.
(viii) Using handkerchief while sneezing and coughing to prevent the spreading of
infectious disease.
Question 9. What is immunisation?
Answer: (i) Immunisation is a process by which human being is made resistant to diseases or become free from any illnesses.
(ii) It can be done by giving vaccine for a disease. This vaccine then stimulates the immune system of body to protect against successive infection.
Question 10. What are the immunisation programmes available at the nearest Health Centre in your locality? Which of these diseases are the major health problems in your area?
Answer: The immunisation programmes available at the nearest Health Centre in our locality are :
(a) Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine
against tuberculosis.
(b) Polio drops against polio.
(c) Vaccination against chicken pox.
(d) Vaccination against hepatitis.
(e) DPT vaccination against diphtheria,
pertussis (whooping cough) and tetanus.
(f) Immunisation against measles.
(ii) The major health problems are hepatitis, tuberculosis, tetanus and chicken pox.
Hope you understand the why do we fall ill ncert solutions class 9. Let us know in comment section.
why do we fall ill class 9 extra questions
Objective type questions
Question 1. Which of the following is dangerous for individual health?
(a) Open drainage
(b) Garbage throw in streams
(c) Stagnant water in our sorroundings
(d) All of the above
Question 2. Which of the following would lead to malnutrition?
(i) Overnutrition
(ii) Undernutrition
(iii) Imbalanced nutrition
(a) only ii
(b) ii and iii
(c) i and iii
(d) i, ii and iii
Question 3. Identify the incorrect match.
(a) Acute disease - cold and cough
(b) Infectious disease - Goistre
(c) Non-infectious disease - Diabetes
(d) Chronic disease - Tuberculosis
Question 4. Complete the analogy given below and choose the correct option.
(a) Protozoan
(b) Bacterial disease
(c) Viral disease
(d) Worm disease
Question 5. Making anti-viral drug is more difficult than making anti-bacterial medicine because
(a) Viruses do not use same pathway as that of bacteria
(b) Viruses are on the border line of living and non-living
(c) Viruses have very few biochemical mechanisms of their own
(d) Viruses have a protien coat
Question 6. Select the Contagious, viral disease from the following
(i) Dengue
(ii) Leprosy
(iii) Common cold
(iv) Chicken pox
(a) i and iii
(b) ii and iv
(c) iii and iv
(d) ii and iii
Question 7. What is common between diarrhoea, cholera and typhoid diseases?
(a) All of them are caused by bacteria
(b) All of them is transmitted by Contaminated food and water
(c) All of them are cured by antibiotics
(d) All of the above
Question 8. The figure given below shows a disease-causing microbe. Choose the correct option for microbe A.
(a) Staphylococci: Bacteria which can cause acne
(b) Leishmania: Protozoan that causes Kala-azar
(c) Ascaris lumbricoides: Also known as round worm
(d) Trypanosoma: Protozoan responsible for sleeping sickness
Question 9. If you live in an overcrowded and poorly Ventilated house, it is possible that you may suffer from which of the following disease?
(a) Cancer
(b) AIDS
(c) Airborne diseases
(d) Cholera
Question 10. Refer to the given picture and choose the correct statement regarding it.
(a) Edward Jenner is known as father of vaccination
(b) Cowpox is a very dangerous disease
(c) Smallpox virus is not related to the Cowpox virus
(d) There are vaccines for all infectious diseases
Very short answer type Questions
Question 1. State any two conditions essential for good health
Question 2. Write Five 'F's of prevention of transmission of disease by maintaining sanitation and hygiene.
Question 3. Public cleanliness is considered more important for individual's health. Do you agree? Give reason.
Question 4. How is personal health and community health connected?
Question 5. Are the conditions essential for maintaining good health and being free of disease same or different? Why?
Question 6. Why are we normally advised to take bland and nourishing food when we are sick?
Question 7. Give two examples of:
(i) Acute diseases
(ii) Chronic diseases
(iii) Infectious diseases
(iv) Non-infectious diseases
Question 8. Give one local and one general effect of inflammation process.
Question 9. Name the viral disease which is about to be completely eradicated from the world. What is it's preventive measure?
Question 10. Give cause and remedy of
(i) Hepatitis
(ii) AIDS
(iii) Malaria
Question 11. Name two types of diseases caused by regularly breathing in the polluted air in the polluted air?
Question 12. Which is the most common vector of disease causing germs? Give example of atleast two diseases transmitted by it.
Question 13. Roshni visited her friend suffering from malaria. What are the chances of her contracting the disease?
Question 14. A lady suffering from AIDS is pregnant. What is the most likely route for the chile to get disease?
Question 15. A person suffering from HIV - AIDS cannot fight even minor infections. Why?
Question 16. Name two diseases that can be prevented by using vaccines.
Question 17. Name the disease in which
(i) Patient fears water
(ii) Skin become yellowish
Question 18. 'Air, water, food and personal contact's - choose the odd one out with respect to hepatitis virus.
Question 19. How do children in many parts of India get immune to hepatitis - A by the time they are five years old?
Question 20. High fever, headache, nausea, vomiting and joint pains are some of the symptoms seen in a patient.
Which disease he might be suffering from? How does it spread?
Short answer type Questions
Question 1. Give any four factors necessary for a healthy person.
Question 2. How is personal health and community health connected?
Question 3. Which disease is more harmful, acute or chronic disease? Why?
Question 4. Classify the following diseases as infectious and Non-infectious:
(i) AIDS
(ii) Tuberculosis
(iii) Cholera
(iv) High blood pressure
(v) Heart disease
(vi) Pneumonia
(vii) Cancer
Question 5. Identify infectious and Non-infectious diseases from the diseases given below:
Tuberculosis, goitre, marasmus and typhoid.
Question 6. Explain, why antibiotics do not work against viruses, but work against many groups of bacteria.
Question 7. Which bacterium causes peptic ulcers? Who discovered the pathogen for the first time?
Question 8. Influenza or common cold, spreads faster and is difficult to control. Explain.
Question 9. How do diseases spread through water?
Question 10. State mode of transmission of
(i) Syphilis
(ii) Tuberculosis
(iii) Jaundice
(iv) Japanese encephalitis
Question 11. Explain, what is organ specific manifestation?
Question 12. Why does a person suffering from HIV, AIDS die, even due to small infection?
Question 13. List the principles of treatment of a discuss.
Question 14. Why is DPT called triple antigen?
Question 15. What causes Japanese encephalitis? How it can be prevented?
Question 16. Identify the microorganism and it's type. Name the disease it causes and the means of its spread.
Question 17. Why is it that one is advised to avoid closed, crowded places like cinema halls during changing weather?
Question 18. A mother, who had suffered from chickenpox in her childhood, is now taking care of her child, who is suffering from the same disease. What are the chances of the mother having chickenpox? Explain.
Question 19. A virus enters the immune system of a patient and damages it's function. Answer the following:
(i) Name the disease patient is suffering from.
(ii) Name the pathogen and two modes of transmission of this virus.
Question 20. Give reason
(i) Wearing socks and full sleeves at night will not prevent the attack from dengue.
(ii) In aslum, many people are reported to be a suffering from malaria.
Question 21. Name the disease/microbe which
(i) Kissing does not spread the disease, while sexual contact transfer the same.
(ii) The bacteria which cause acne.
(iii) Virus which targets the liver.
(iv) Disease occurs by saliva of infected animal.
Question 22. If Penicillin is given to a patient suffering from Jaundice, it does not have any effect on the infection. Why?
Question 23. A person was bitten by a stray dog. After some days his nature gets irritated, he started fearing water.
(i) Name the disease
(ii) Is there any vaccine available?
(iii) Is there any plan of your local authority for the control of the disease?
Question 24. Give an account of malaria, giving it's causative agent, symptoms and control measures.
Question 25. A person is suffering from loss of appetite with feeling of nausea and is passing dark yellow urine. Identify the disease and suggest any two methods of preventing it and two methods of controlling it.
Question 26. (i) Name the causal organisms of swine flue?
(ii) Suggest two measures that the local authorities of your neighborhood should take to bring down the incidence of diseases like malaria, typhoid and dengue?
Question 27. A rabid dog was seen in a colony and everyone was afraid of going near it. Name the disease and state how this disease is transmitted. The dog is presently considered the reservoir of the disease. What is the meaning of 'reservoir' here?
Question 28. Amit started sneezing and wheezing after reaching Shimla, from Delhi. But on return, the symptoms disappeared. What is such a response called? How does the body produce it?
Question 29. Explain, how body reacts after the entry of microbes in the body.
Question 30. Why is AIDS considered to be a 'syndrome' and not a disease?
Long answer type Questions
Question 1. Explain by giving reasons.
(i) Balanced diet is necessary for maintaining healthy body.
(ii) Health of an organisms depends upon the sorroundings environmental conditions.
(iii) Our sorroundings should be free from stagnant water.
(iv) Social harmony and good economic conditions are necessary for good health.
Question 2. Explain the following statements
(i) Being disease-free is not the same as being healthy.
(ii) Villagers suffer with cholera more than urban areas.
(iii) Community health is essential for good individual health.
Question 3. What are the causes and symptoms of malaria? How can it be prevented and controlled?
Question 4. What precautions will you take to justify 'Prevention is better than cause'?
Question 5. Explain the statement by giving two example:
'It is not necessary that the pathogen may effect an organ or tissue depending upon the point of entry.'
Question 6. (i) State two examples of viral diseases.
(ii) After an injury an injection is given immediately. What is it and why is it given?
Question 7. Mr. Lyer had could and throat infection. Doctor prescribed an antibiotic.
(i) Which pathogens could have caused the infection?
(ii) What is the mode of action of antibiotics? Mr. Lyer recovered from cold but he still had throat infection. Would the doctor continue the antibiotic further? State yes or no giving reason.
FAQ (frequently asked questions)
Question
What is meant by symptoms of disease?
Answer:
Symptoms of disease are the things we feel as being 'wrong' like headache, cough etc. These indicate that there may be a disease but they do not exactly indicate what the disease is but they narrow the possibilities of certain diseases. Symptoms are felt by the host body and can't be seen by anyone else.
Question
What are the conditions essential for good health?
Answer:
Basic conditions for good health
(i) Proper balanced and nutritious diet
(ii) Personal hygiene
(iii) Clean environment and sorroundings
(iv) Healthy air, no pollution in the sorroundings
(v) Regular exercise
(vi) Proper rest
(vii) Good standard of living and economic status
Question
What are the different ways by which infectious spread?
Answer:
Infectious diseases can spread to healthy person from infected person by:
- Direct contact
- By air
- Indirect contact
- By food
- Mosquito
- Insect
- Rabid animal
Question
Explain the concept of immunisation covered in the chapter 13 of Ncert why do we fall ill?
Answer:
If you had smallpox once, there was no chance of suffering from it again .So, having the disease once was a means of preventing subsequent attacks of the same disease. This happens because when the immune system first sees an infectious microbe, it responds against it and then remembers it specifically. So the next time that particular microbe, or its close relatives enter the body, the immune system responds with even greater vigour. This eliminates the infection even more quickly than the first time around. This is also known as immunisation.
Question
What are the main topics and sub topics students have to covered in the chapter why do we fall ill? Of Ncert class 9.
Answer:
Main topics from why do we fall ill class 9:
- Helath
- Personal and community health issues
- Disease
- Infectious Diseases
- Immunisation
- Pulse Polio Programme
Main subtopics from why do we fall ill class 9:
- Factors affecting an individuals Health
- Manifestations of disease
- Causes of disease
- Infectious and Non-infectious diseases
- Infectious agents
- Means of spread of infectious Disease
- General effects of infectious Diseases
- Organ-specific and Tissue-specific Manifestations
- Principles of treatment
- Antibiotics
- Principles of prevention
Question
Why do you need to do class 9 Biology chapter 13 Ncert solutions?
Answer:
After completing the chapter and understanding the concept you have to do some practice of it and ncert is the only book from where you can get best and relevant questions in the form of Ncert solutions.
Question
How can I score well by solving Ncert solutions from the chapter 13 class 9 why do we fall ill?
Answer:
If you want to score well in your examination you have to complete your ncert book and practice it's solved examples of the book because most of the question are directly asked from Ncert in the cbse exams.
Conclusion
Hope you like our article in which we had provide you Notes of why do we fall ill class 9 and why do we fall ill class 9 extra questions with ncert solutions. Let us know in comm
Also read










Post a Comment
If you have any doubt or need any study material comment.