Why to choose our notes?
- Used funny memes in it
- Funny and easy in language
- You will never get bored from it
- All exam related topics are covered
- We use both english and hinglish language in our notes
- Free pdf is available
| Class | 10th |
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Chapter | Chapter 10 |
| Chapter name | Light reflection and refraction |
| Category | Class 10th notes |
Class 10 light notes pdf - Free Ebook download
Light reflection and refraction class 10 - Introduction
In the chapter light: reflection and refraction we are going to study about the phenomena of reflection and refraction. Where in reflection we will study about how travels and reflect from several mirrors like plane mirror and spherical mirrors. we will also relate the thing to our real life so that we can understand the concepts very clearly.
Important topics under CBSE Class 10 science chapter 10 - Light reflection
- What is Reflection?
- Reflection by spherical mirrors
- Rules of image formation
- Image formation by convex and concave mirrors using ray diagrams
- Sign convention, mirror formula and magnification
Note-> Plz rotate your phone to read the Notes.
📚Notes of Light📚
🔶Light is an energy which enables the sensation of
vision.
Standard definition
Light is an electromagnetic form of energy or a
series of photon Particles which enable us to
see different objects.
🔶Dual Nature of Light (light ka doglapan)
There are two theories about light
🔸Wave theory:According to this light consists of electromagnetic
waves which do not require a medium for
their propagation.
🔸Particle theory:According to this light is composed of particles
which travel in a straight line at a very high
speed. The particle is known as a photon.
Properties of light
🔸 It does not require any medium to travel.
🔸The speed of light is tremendous
3x10^8 m/s
🔸Every next particle follows the other one.Reflection of light
🔶When a light ray comes from a medium that
strikes any surface and bounces back into the same medium, this phenomenon is known as
"Reflection of light".
Laws of Reflection (For any mirror)
🔶The angle of incidence is always equal to the
angle of reflection. ∠i = ∠r
🔶The incident ray, Normal and reflected ray all lie
on the same plane. They all join at a point
known as the point of incidence.
🔶Properties of image formed by a plane mirror
🔸The image formed is Virtual & Erect
🔸The size of image object is equal to the size of
object
🔸The distance of the object from the mirror is
equal to the distance of the image from mirror
🔸The image formed is laterally inverted
Spherical mirrors
🔶A mirror whose reflecting surface is a part of a
hollow sphere of glass is known as a spherical
mirror.
🔸A spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is bulging out is known as a
Convex mirror.
🔸A spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is
bent-in is known as a Concave mirror.
Terms related to spherical mirror
🔶Center of Curvature -It is the centre of the hollow sphere of the glass of
which the mirror is a part.
🔶Radius of Curvature - It is the radius of the hollow sphere of glass of
which the mirror is a part.
🔶Pole - The central point of the surface of the mirror is
called its pole.
🔶Principal axis - It is a line passing through the center of curvature
and the pole of the mirror.
🔶Aperture - It is the portion of mirror through which r
eflection of light actually takes place.
🔶Principal FocusIt is the point where all the rays which are parallel
and close to the principal axis converge
(or appear to converge).
🔶Focal length - It is the distance between the Pole and Principal
focus of the mirror.
Concave mirror
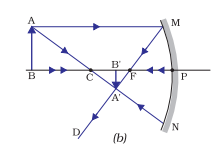
🔶Rules for image formation by Concave mirror
🔸When a light ray strikes the mirror parallel to the
principal axis it passes through the focus after reflection.
🔸When a light ray strikes the mirror passing
through the focus it is reflected parallel to the
principal axis.
🔸When a passing light strikes the mirror through
the centre of curvature it is rebounded on its
own path.
Image formation by Concave mirror
🔶Case I (Object is at Infinity)
Position: At F
Size: Highly diminished Or point sized
🔶Case II (Object is Beyond C)
Nature: Real and Inverted
Position: Between F and C
Size: Diminished
🔶Case III (Object is at C)
Nature: Real and Inverted
Position: At C
Size: Same size
🔶Case IV (Object between C and F)
Nature: Real and Inverted
Position: Beyond C
Size: Enlarged
🔶Case V (Object is at F)
Nature: Real and Inverted
Position: At Infinity
Size: Highly enlarged
🔶Case VI (Object is between P and F)
Nature: Virtual and Erect
Position: Behind the mirror
Size: Enlarged
Uses of Concave Mirrors
🔸It is used as a shaving mirror to see a large image
of the face.
🔸It is used as reflectors in torches, headlights.. etc.
🔸Used by dentists to obtain a larger view of teeth.
Convex Mirror
🔶Rules for Image formation by Convex Mirror
🔸When a light ray strikes the mirror parallel to the principal axis it appears to be coming from the
Focus.
🔸When a light ray going towards the centre of
curvature strikes the mirror it retraces its own
path.
🔸when a light ray going towards the Focus of
mirror strikes the object it is reflected parallel to
the principal axis.
🔸when a light ray strikes the mirror at pole it is
reflected at the same angle.
Formation of image in Convex mirror
🔶Case I (Object is at Infinity)
Nature: Virtual and erect
Position: At F
SIze: Highly diminished
🔶Case II (Object is anywhere on principal axis)
Nature: Virtual & Erect
Position: between F and P
Size: Diminished
Uses of Convex mirrors
🔸Used as rear view mirrors in vehicles to see a
wider view of traffic.
🔸Convex mirrors are used in shops as Security
mirrors.
Sign Convention for Spherical Mirrors
🔸The pole of the mirror is taken as Origin.
🔸All the distances which are on the right side of
the mirror are measured as positive.
🔸All the distances which are on the left side of the
mirror are measured as negative.
🔸All the distances which are measured
perpendicular and upwards of the principal axis
are marked as Positive.
Mirror formula and Magnification
🔶The formula which gives the relationship
between image image distance (v), object distance
(u), focal length (f) of spherical mirrors is known
as mirror formula.
🔶Linear magnification is the ratio of image and
height of object.
🔸M is smaller than 1 the image formed is
diminished.
❇THE END❇
Important terms in class 10th light reflection
Center of Curvature - It is the centre of the hollow
sphere of the glass of which the mirror is a part.
Radius of Curvature - It is the radius of the hollow sphere of glass of
which the mirror is a part.
Pole - The central point of the surface of the mirror is
called its pole.
Principal axis - It is a line passing through the center of curvature
and the pole of the mirror.
Aperture - It is the portion of mirror through which
reflection of light actually takes place.
Principal Focus - It is the point where all the rays
which are parallel and close to the principal
axis converge (or appear to converge).
Focal length - It is the distance between the Pole and Principal
focus of the mirror.
FAQ (frequently asked questions from class 10h chapter light)
Question
What is light class 10?
Answer
Light is an electromagnetic form of energy or a
series of photon Particles which enable us to
see different objects.
Question
What is reflection of light class 10?
Answer
When a light ray comes from a medium that strikes
any surface and bounces back into the
same medium, this phenomenon is known as
"Reflection of light".
Question
What Are the main topics in light class 10?
Answer
- What is Reflection?
- Reflection by spherical mirrors
- Rules of image formation
- Image formation by convex and concave mirrors using ray diagrams
- Sign convention, mirror formula and magnification
- Reflection of light
- Refraction of light
- Dispersion of light
- Scattering of light
| Post | Link |
|---|---|
| Science chapter 1 notes | Click here |
| Class 10 maths strategy | Click here |
| Class 10 power sharing notes | Click here |
Thanks for using our notes and please let us know in comment section about your experience on the Notes of light class 10th. Also please join our social media paltforms so that u stay up to date.
.jpg)









Post a Comment
If you have any doubt or need any study material comment.