Depending upon the direction of displacement and force applied work can be zero, positive or negative.
The Energy of a body due to its position or change in shape is known as potential energy. An object when gains energy may store it in itself as potential energy.
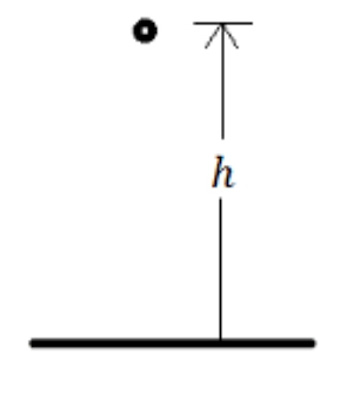
P.E. ∝ h (does not depend on the path follows) Greater the height, greater is the P.E.
We know that when an object rises above the ground some work is done against gravity. Because the work is done, the object would gain some energy.
The energy that object gains at a height is called Gravitational Potential Energy.
Sum of Kinetic and potential energy of an object is known as mechanical energy.
The change of one form of energy to another form of energy is known as transformation of Energy.
- At hydroelectric power house, the potential energy of water is transformed into Kinetic energy and then into electric energy.
- Plants use solar energy (sun) to make chemical energy in food by the process of photosynthesis.
■ Law of Conservation of Energy
According to the law of conservation of energy, total amount of energy before and after transformation remains same.
Although some energy may be wasted during conversion but the total energy of the system remains same.
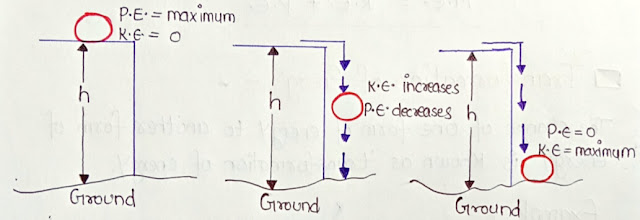
● Conservation of energy during freefall
Consider following example where an object of mass 'm' is fall freely from height 'h'.
We can see that the sum of Kinetic and Potential energy at every instant is Constant. We can say the energy is conserved during transformation.
■ Power
The rate of doing work is defined as power.
Power = work done/Time taken or P = W/T
● unit of power = watt (W) = 1 Joule/sec
Average power:
Total work done or Total energy used/ Total time taken
■ Commercial Unit of Power
We cannot use Joule to measure power commercially. Instead, we use kilowatt-hour (kwh)
Commercial unit of energy = 1 kilowatt hour (kwh)
∴ 1 kwh = 3.6 × 10^6J (important)
1 Kwh: 1 Kwh is the amount of energy consumed when an electric appliance having a power rating of 1 kilowatt is used for 1 hour.
Hope you like the work and energy class 9 notes. Let us know it in comment section. Thank you so much!!
class 9 science extra questions and Work And Energy Class 9 MCQ that will help you to practice and revise the importance topics of the chapter work and energy.
class 9 science extra questions
Short Answer Questions
Question No 1.
A rocket is going upward with a velocity v. If the velocity of this rocket is suddenly tripled, what will be the ratio of two kinetic energies?
Question No 2.
Rohit can run with a speed of 8 m s–1 against the frictional force of 10 N,and Aryan can move with a speed of 3 m s–1 against the frictional force of 25 N.Who is more powerful and why?
Question No 3.
A girl is moving on a straight road against a frictional force of 5 N. After travelling a distance of 1.5 km he forgot the correct path at a roundabout of radius 100 m. However,she moves on the circular path for one and half cycle and then he moves forward upto 2.0 km.Calculate the work done by her.
Question No 4.
Can any object have mechanical energy even if its momentum is zero? Explain.
Question No 5.
The weight of a lady on a planet A is about half that on the earth. She can jump upto 0.4 m height on the surface of the earth. How high She can jump on the planet A?
Question No 6.
The velocity of an object moving in a straight line is increased by applying a constant force F, for some distance in the direction of the motion. Prove that the increase in the kinetic energy of the object is equal to the work done by the force on the body.
Question No 7.
Is it possible that a body is in the state of accelerated motion due to external force acting on it, but no work is being done by the force. Explain it with an example.
Question No 8.
A Tennis ball is dropped from a height of 10 m. If the energy of the ball reduces by 40% after striking the ground, how much high can the ball bounce back? (g = 10 m s–2)
Question No 9.
If an electric iron of 1200 W is used for 30 minutes everyday, find electric energy consumed in the month of December.
Class 9 science extra questions
Long Answer Questions
Question No 1.
A light and a heavy object have the same momentum. Find out the ratio of their kinetic energies. Which one has a larger kinetic energy?
Question No 2.
An automobile engine propels a 1000 kg car (A) along a levelled road at as peed of 36 km h–1. Find the power if the opposing frictional force is 100 N. Now, suppose after travelling a distance of 200 m, this car collides with another stationary car (B) of same mass and comes to rest. Let its engine also stop at the same time. Now car (B) starts moving on the same level road without getting its engine started. Find the speed of the car (B) just after the collision.
Question No 3.
A girl having mass of 35 kg sits on a trolley of mass 5 kg. The trolley is given an initial velocity of 4 m s–1 by applying a force. The trolley comes to L rest after traversing a distance of 16 m. (a) How much work is done on the trolley? (b) How much work is done by the girl?
Question No 4.
Four men lift a 250 kg box to a height of 1 m and hold it without raising or lowering it. (a) How much work is done by the men in lifting the box? (b) How much work do they do in just holding it? (c) Why do they get tired while holding it? (g = 10 m s–2)
Question No 6.
What is power? How do you differentiate kilowatt from kilowatt hour? The jog Falls in Karnataka state are nearly 20 m high. 2000 tonnes of water falls from it in a minute. Calculate the equivalent power if all this energy can be utilized? (g = 10 m s–2)
Question No 7.
How is the power related to the speed at which a body can be lifted? How many kilograms will a man working at the power of 100 W, be able to lift at constant speed of 1 m s–1 vertically? (g = 10 m s–2)
Question No 8.
Define watt. Express kilowatt in terms of joule per second. A 150 kg car engine develops 500 W for each kg. What force does it exert in moving the car at a speed of 20 m s–1?
Question No 9.
Compare the power at which each of the following is moving upwards against the force of gravity? (given g = 10 m s–2)
(i) a butterfly of mass 1.0 g that flies upward at a rate of 0.5 m s–1.
(ii) a 250 g squirrel climbing up on a tree at a rate of 0.5 m s–1.
Class 9 work and energy extra questions Solutions are not provided so that you can solve these by your own.
Work And Energy Class 9 MCQ
Multiple Choice Questions
1. When a body falls freely towards the earth, then its total energy
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) remains constant
(d) first increases and then decreases
Answer: (c) remains constant
2. A car is accelerated on a levelled road and attains a velocity 4 times of its initial velocity. In this process the potential energy of the car
(a) does not change
(b) becomes twice to that of initial
(c) becomes 4 times that of initial
(d) becomes 16 times that of initial
Answer: (a) does not change
3. In case of negative work the angle between the force and displacement is
(a) 0° (b) 45° (c) 90° (d ) 180°
Answer: (d) 180°
4. An iron sphere of mass 10 kg has the same diameter as an aluminium sphere of mass is 3.5 kg. Both spheres are dropped simultaneously from a tower. When they are 10 m above the ground, they have the same
(a) acceleration
(b) momenta
(c) potential energy
(d) kinetic energy
Answer: (a) acceleration
5. A girl is carrying a school bag of 3 kg mass on her back and moves 200 m on a levelled road. The work done against the gravitational force will be (g =10 m s–2)
(a) 6 ×103 J
(b) 6 J
(c) 0.6 J
(d) zero
Answer: (d) zero
6. Which one of the following is not the unit of energy?
(a) joule
(b) newton metre
(c) kilowatt
(d) kilowatt hour
Answer: (c) kilowatt
Hope you like the Work And Energy Class 9 MCQ, class 9 science extra questions and class 9 work and energy notes. Let us know in comment section.
FAQ (Frequently asked questions)
Question
What is work?
Answer:
The definition of work done may vary in real life and scientifically. For Example, we may consider studying, talking, singing as work but it is not so in the case of science.
Question
What is Energy?
Answer:
The capacity of doing work is called energy. The object can gain or lose energy depending upon the work done. If an object does some work it loses its energy and if some work is done on an object it gains Energy.
Question
What is Kinetic energy?
Answer:
Every moving body have some energy called kinetic energy.
OR
The energy of a body due to its motion is called Kinetic energy.
Question
What is the formula for Kinetic energy?
Answer:
W = ½ mv^2 = K = ½ mv^2
Work done = change in Kinetic energy
Question
What is Potential energy?
Answer:
The Energy of a body due to its position or change in shape is known as potential energy. An object when gains energy may store it in itself as potential energy.
Question
What is Mechanical Energy?
Answer:
Sum of Kinetic and potential energy of an object is known as mechanical energy.
M.E. = K.E + P.E.
Question
What is Power?
Answer:
The rate of doing work is defined as power.
Power = work done/Time taken or P = W/T
Question
Is term 2 is MCQ based?
Answer:
Because of rise of corona cases there is no update from cbse about the exam pattern, If exam held offline it will be subjective based and If exam held online it will be objective based.
Question
What is the class 9 term 2 science syllabus?
Answer:
Class 9 term 2 science syllabus contain 5 chapte Answer: rs:
ATOMS AND MOLECULES
STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM
GRAVITATION
WORK AND ENERGY
WHY DO WE FALL ILL?
Question
Which reference book is good for class 9 term 2?
Answer:
The following books are useful for class 9 term 2:
Oswaal question bank
Arihant sample papers
Exemplar
Social media links
Also read:
Thank your for reading the article till the last and hope you fully understand the work and energy class 9 notes. Lets us know in comment section.


Post a Comment
If you have any doubt or need any study material comment.